Benefits of load balancing Hyland OnBase
The top three benefits of load balancing Hyland OnBase, whether for application/web servers or for Workflow processing, are:
- Optimized performance and reduced latency: By distributing incoming user requests and processing workloads across multiple servers, load balancing ensures that no single server becomes overwhelmed. This prevents performance bottlenecks, resulting in quicker response times for users accessing documents, running processes, or interacting with the system. It ensures all available OnBase resources (servers) are utilized efficiently, leading to better overall throughput and a smoother user experience, especially during peak usage.
- High Availability (HA): Load balancing is crucial for creating a highly available OnBase environment. If one OnBase server or component fails (goes offline due to a hardware issue, maintenance, etc.), the load balancer automatically detects the failure and redirects all traffic to the remaining healthy servers. This failover capability ensures that the OnBase system remains accessible and operational, supporting business continuity and minimizing disruptions for end-users.
- Enhanced scalability: Load balancing provides the flexibility to grow your OnBase environment as your organization’s needs increase. As your number of users, documents, or transactions grows, you can simply add new OnBase servers to the load-balanced pool. The load balancer automatically starts distributing traffic to the new servers. This enables an organization to scale their OnBase infrastructure horizontally, ensuring the system can handle future growth without requiring a complete system overhaul.
About Hyland OnBase
Hyland OnBase is a single enterprise information platform designed to manage your content, processes and cases. Centralizing your important business content in one secure location.
In environments with multiple OnBase servers load balancing is required to ensure High Availability.
Why Loadbalancer.org for Hyland OnBase?
Loadbalancer’s intuitive Enterprise Application Delivery Controller (ADC) is designed to save time and money with a clever, not complex, WebUI.
Easily configure, deploy, manage, and maintain our Enterprise load balancer, reducing complexity and the risk of human error. For a difference you can see in just minutes.
And with WAF and GSLB included straight out-of-the-box, there’s no hidden costs, so the prices you see on our website are fully transparent.
More on what’s possible with Loadbalancer.org.
How to load balance Hyland OnBase
The load balancer can be deployed in 4 fundamental ways: Layer 4 DR mode, Layer 4 NAT mode, Layer 4 SNAT mode, and Layer 7 Reverse Proxy (Layer 7 SNAT mode).
For Hyland OnBase, Layer 7 Reverse Proxy is recommended.
Virtual service (VIP) requirements
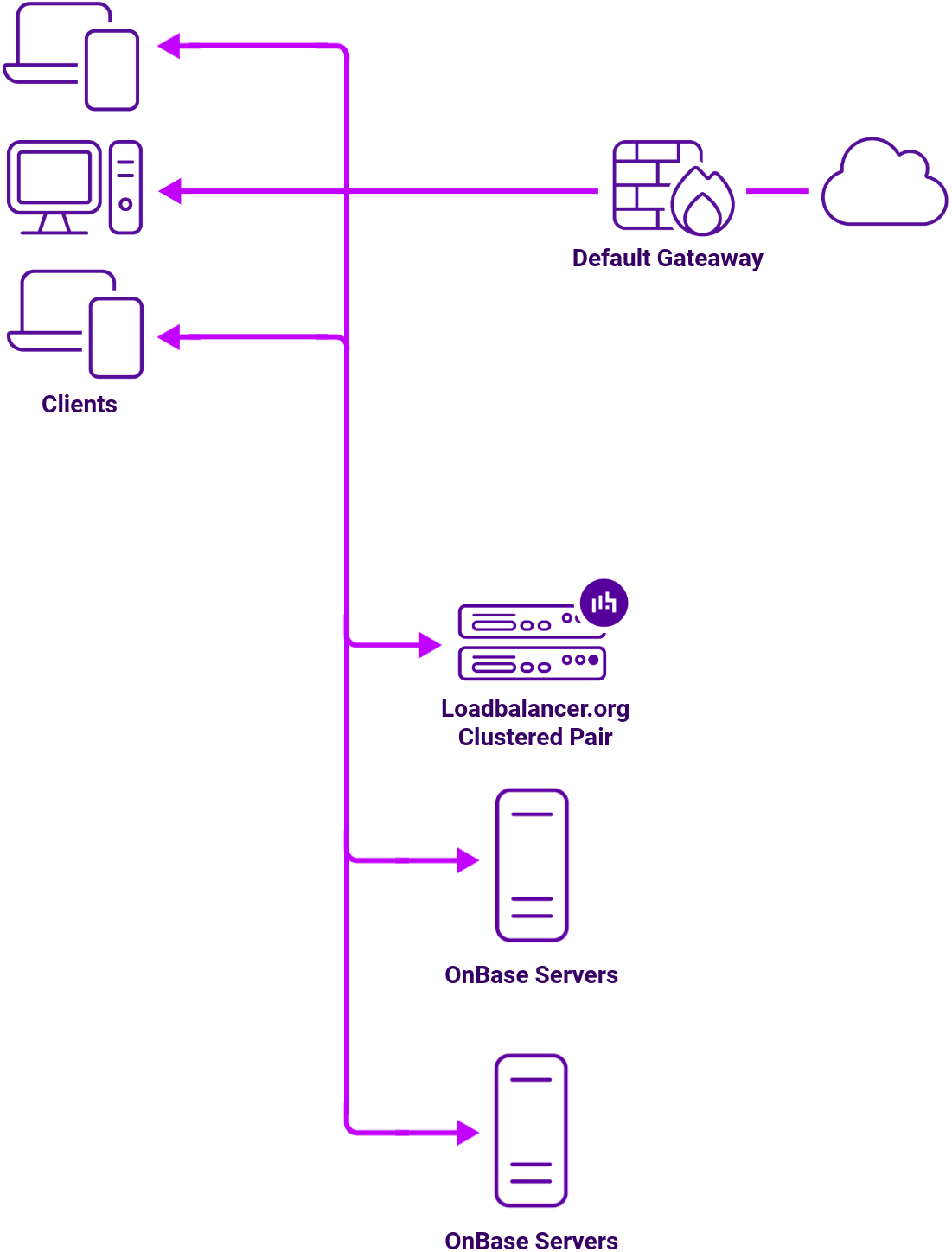
To provide load balancing and HA for Hyland OnBase, multiple Web Servers and Application Servers are load balanced and the following VIPs are required:
| Ref. | VIP Name | Use | Mode | Port(s) | Persistence Mode | Health Checks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref. | VIP Name | Use | Mode | Port(s) | Persistence Mode | Health Checks |
| VIP 1 | WebServers | Web Server traffic | Layer 7 Reverse Proxy | 80 | HTTP Cookie | HTTP (GET) |
| VIP 2 | AppServers | App Server traffic | Layer 7 Reverse Proxy | 80 | HTTP Cookie | HTTP (GET) |
Load balancing deployment concept
About Layer 7 Reverse Proxy
Layer 7 Reverse Proxy uses a proxy (HAProxy) at the application layer. Inbound requests are terminated on the load balancer and HAProxy generates a new corresponding request to the chosen Real Server. As a result, Layer 7 is typically not as fast as the Layer 4 methods.
Layer 7 is typically chosen when enhanced options such as SSL termination, cookie based persistence, URL rewriting, header insertion/deletion etc. are required, or when the network topology prohibits the use of the Layer 4 methods.
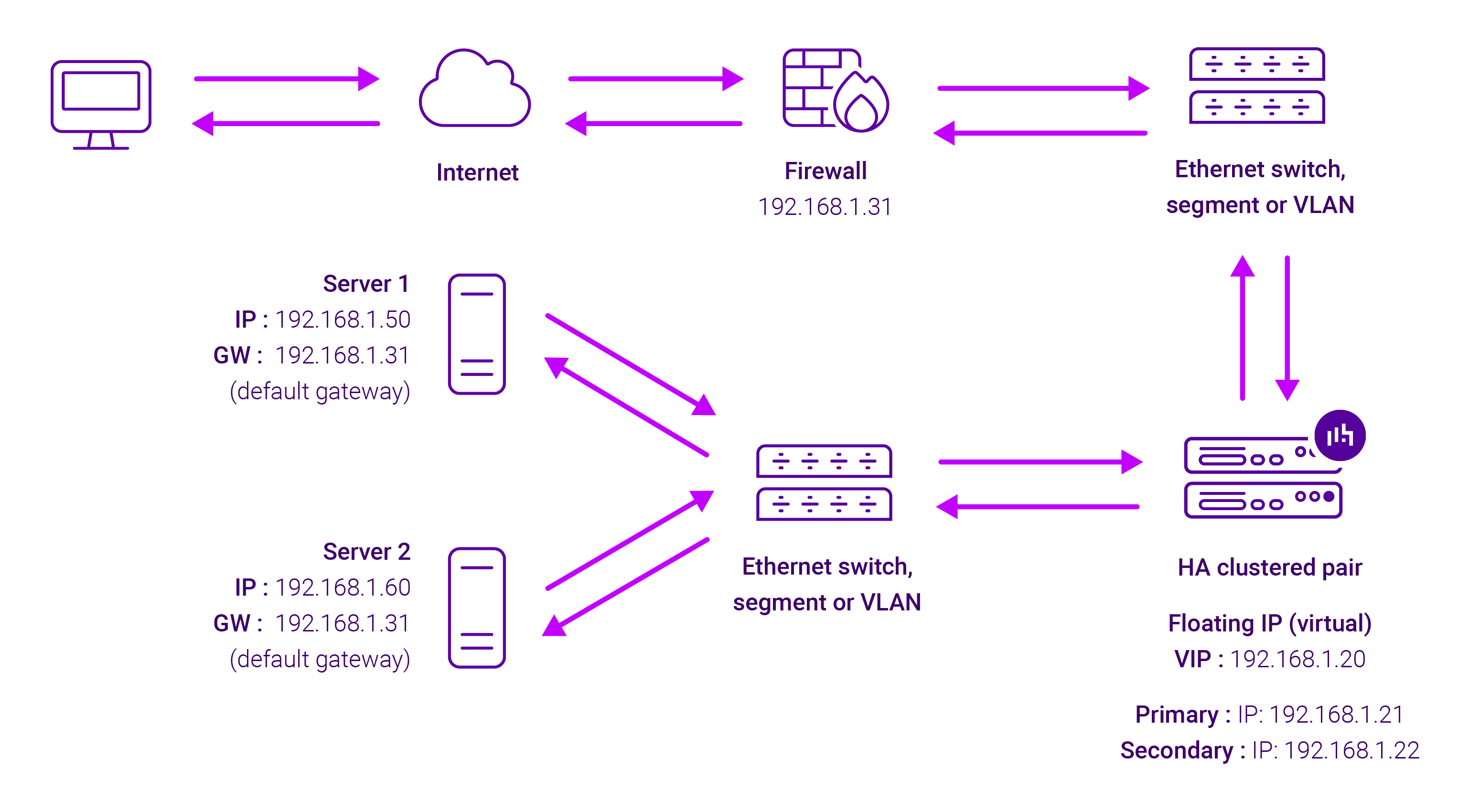
Because Layer 7 Reverse Proxy is a full proxy, any server in the cluster can be on any accessible subnet, including across the Internet or WAN.
Layer 7 Reverse Proxy is not transparent by default i.e. the Real Servers will not see the source IP address of the client, they will see the load balancer’s own IP address by default, or any other local appliance IP address if preferred (e.g. the VIP address). This can be configured per Layer 7 VIP.
If required, the load balancer can be configured to provide the actual client IP address to the Real Servers in two ways:
- Either by inserting a header that contains the client’s source IP address, or
- By modifying the Source Address field of the IP packets and replacing the IP address of the load balancer with the IP address of the client.
Layer 7 Reverse Proxy mode can be deployed using either a one-arm or two-arm configuration. For two-arm deployments, eth0 is normally used for the internal network and eth1 is used for the external network, although this is not mandatory.
No mode-specific configuration changes to the load balanced Real Servers are required.
Port translation is possible with Layer 7 Reverse Proxy e.g. VIP:80 → RIP:8080 is supported. You should not use the same RIP:PORT combination for Layer 7 Reverse Proxy VIPs and Layer 4 SNAT mode VIPs because the required firewall rules conflict.