Load balancing Sage Enterprise Management
Benefits of load balancing Sage Enterprise Management
Load balancing Sage Enterprise Management provides the following benefits:
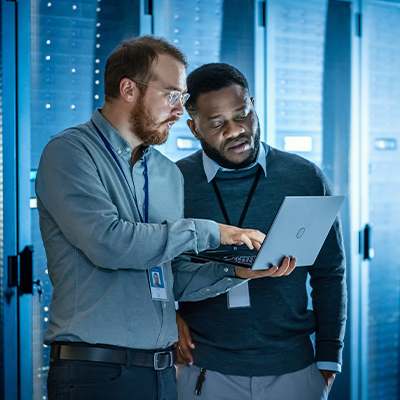
- High Availability (HA): Load balancing is essential for business continuity by eliminating a single point of failure. It allows you to deploy multiple Sage Enterprise Management servers (e.g., application servers and process servers). If one server fails or becomes unhealthy, the load balancer automatically directs all traffic to the remaining healthy servers. This failover mechanism ensures that the critical ERP system remains accessible and operational, minimizing downtime that could otherwise halt core business processes like financial management, manufacturing, or distribution.
- Optimized performance and responsiveness: By efficiently distributing the user workload, load balancing maximizes the system’s overall performance. It prevents any single server from becoming a bottleneck during periods of high user activity or intensive processing (like month-end closing or large data imports).
By balancing requests evenly across available resources, the average response time for user interactions and queries is reduced, leading to a faster and more consistent experience for all users. This optimizes resource usage and maximizes throughput. - Scalability and flexibility: Load balancing enables you to easily adapt your Sage Enterprise Management infrastructure to changing business needs. As your user base grows or your transaction volume increases, you can easily add more application servers to the server pool behind the load balancer. The load balancer instantly begins distributing traffic to the new servers, allowing the system to scale out without any service disruption. Servers can also be taken offline for maintenance, updates, or upgrades (e.g., applying Sage X3 patches) without affecting system availability. The load balancer simply reroutes traffic away from the server undergoing maintenance.
About Sage Enterprise Management
Sage Enterprise Management (formerly known as Sage X3) is an ERP software suite that includes integrated functionality for financial management, sales, customer service, distribution, inventory, and manufacturing, and business intelligence.
Why Loadbalancer.org for Safe Enterprise Management?
Loadbalancer’s intuitive Enterprise Application Delivery Controller (ADC) is designed to save time and money with a clever, not complex, WebUI.
Easily configure, deploy, manage, and maintain our Enterprise load balancer, reducing complexity and the risk of human error. For a difference you can see in just minutes.
And with WAF and GSLB included straight out-of-the-box, there’s no hidden costs, so the prices you see on our website are fully transparent.
More on what’s possible with Loadbalancer.org.
How to load balance Sage Enterprise Management
The load balancer can be deployed in 4 fundamental ways: Layer 4 DR mode, Layer 4 NAT mode, Layer 4 SNAT mode, and Layer 7 Reverse Proxy (Layer 7 SNAT mode).
For load balancing Sage Enterprise Management we usually recommend Layer 7 Reverse Proxy.
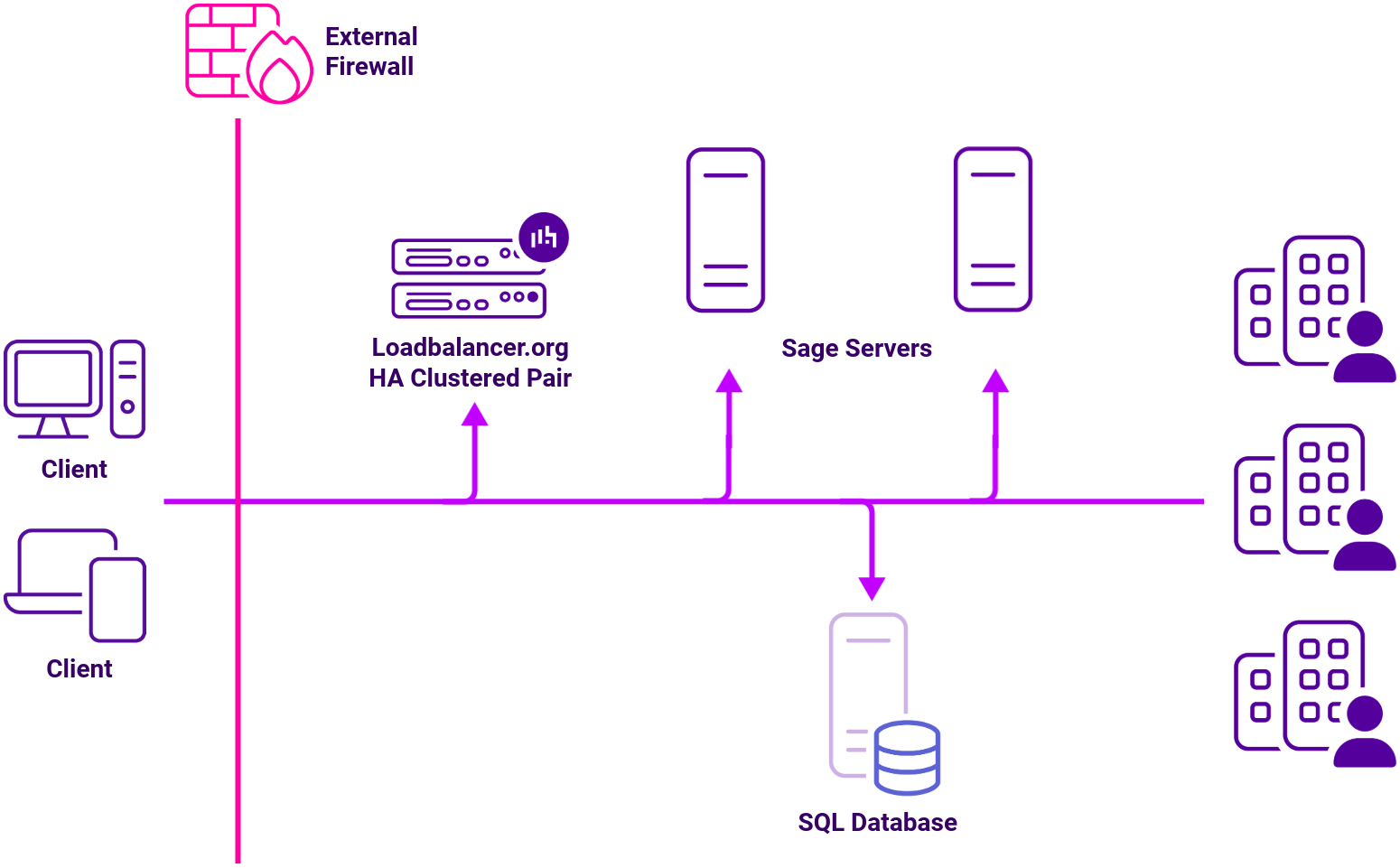
Virtual service (VIP) requirements
To provide load balancing and HA for Sage X3 ERP, only a single VIP is required:
- X3
Port requirements
| Port | Protocols | Use |
|---|---|---|
| 8124 | TCP/HTTP | X3 web services |
Load balancing deployment concept
About Layer 7 Reverse Proxy
Layer 7 Reverse Proxy uses a proxy (HAProxy) at the application layer. Inbound requests are terminated on the load balancer and HAProxy generates a new corresponding request to the chosen Real Server. As a result, Layer 7 is typically not as fast as the Layer 4 methods.
Layer 7 is typically chosen when enhanced options such as SSL termination, cookie based persistence, URL rewriting, header insertion/deletion etc. are required, or when the network topology prohibits the use of the Layer 4 methods.
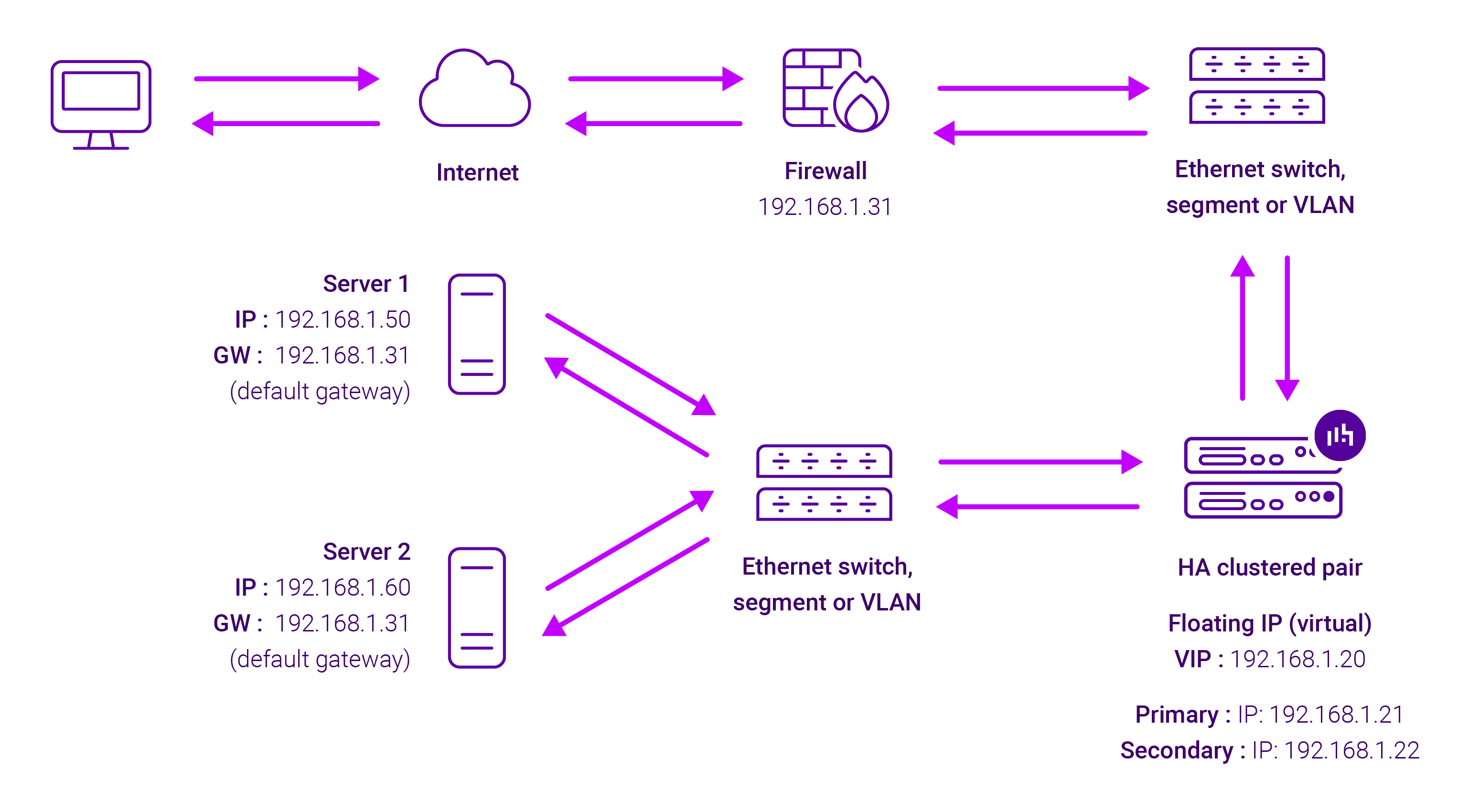
Because Layer 7 Reverse Proxy is a full proxy, any server in the cluster can be on any accessible subnet, including across the Internet or WAN.
Layer 7 Reverse Proxy is not transparent by default i.e. the Real Servers will not see the source IP address of the client, they will see the load balancer’s own IP address by default, or any other local appliance IP address if preferred (e.g. the VIP address). This can be configured per Layer 7 VIP.
If required, the load balancer can be configured to provide the actual client IP address to the Real Servers in two ways:
- Either by inserting a header that contains the client’s source IP address, or
- By modifying the Source Address field of the IP packets and replacing the IP address of the load balancer with the IP address of the client.
Layer 7 Reverse Proxy mode can be deployed using either a one-arm or two-arm configuration. For two-arm deployments, eth0 is normally used for the internal network and eth1 is used for the external network, although this is not mandatory.
No mode-specific configuration changes to the load balanced Real Servers are required.
Port translation is possible with Layer 7 Reverse Proxy e.g. VIP:80 → RIP:8080 is supported. You should not use the same RIP:PORT combination for Layer 7 Reverse Proxy VIPs and Layer 4 SNAT mode VIPs because the required firewall rules conflict.