Benefits of load balancing SwiftStack
Load balancing SwiftStack offers the following benefits:
- High Availability and redundancy: Load balancing is critical for fault tolerance and high availability (HA). It performs continuous health checks on all the SwiftStack proxy and storage nodes. If a node fails, goes offline for maintenance, or becomes unhealthy, the load balancer automatically stops sending requests to it. This ensures that clients only interact with functioning nodes, guaranteeing uninterrupted service and preventing a single point of failure from causing downtime.
- Optimized performance: By intelligently distributing client requests, load balancing prevents any single SwiftStack component from becoming a bottleneck, thus maximizing performance. It uses algorithms (like Least Connections or Round Robin) to spread the workload evenly across multiple proxy servers. This equal utilization prevents server overload and improves the responsiveness of the storage system, leading to faster data access and lower latency for users and applications.
- Seamless scalability: Load balancing facilitates horizontal scaling, allowing the SwiftStack cluster to grow on demand without service interruption. As data volume or user traffic increases, administrators can simply add new proxy or storage nodes to the cluster. The load balancer automatically recognizes the new resources and begins routing traffic to them, enabling the infrastructure to handle increasing demands without complex manual reconfiguration.
About SwiftStack
SwiftStack innovations provide Enterprise businesses with flexible data management migration services across multi-cloud infrastructure. Universal access across on-premise and public environments enables fast and accurate insights from data, increasing mobility and collaboration.
Why Loadbalancer.org for SwiftStack?
Loadbalancer’s intuitive Enterprise Application Delivery Controller (ADC) is designed to save time and money with a clever, not complex, WebUI.
Easily configure, deploy, manage, and maintain our Enterprise load balancer, reducing complexity and the risk of human error. For a difference you can see in just minutes.
And with WAF and GSLB included straight out-of-the-box, there’s no hidden costs, so the prices you see on our website are fully transparent.
More on what’s possible with Loadbalancer.org.
How to load balance SwiftStack
SwiftStack Storage architecture supports High Availability (HA) clustering by putting a load balancer in front of it.
Load balancers monitor and perform health checks on a node to ensure traffic is routed correctly to healthy nodes. Without the use of a load balancer, an offline or failed node would still receive traffic, causing failures.
For load balancing Swiftstack Storage we recommend Layer 4 Direct Routing (DR) mode, sometimes referred to as Direct Server Return (DSR). However, Layer 4 NAT, Layer 4 SNAT and Layer 7 SNAT can also be used.
The best method for your deployment depends on a variety of factors. Layer 4 DR mode is fastest, but requires the ARP problem to be solved, and the application running on the real servers to respond both to its own IP address and the VIP. Layer 4 NAT mode requires the default gateway on the real servers to be the load balancer. Layer 4 SNAT mode doesn’t require real server changes, but unlike the other Layer 4 methods, is non-transparent. Layer 7 Reverse Proxy is also non-transparent and requires no real server changes – but it doesn’t offer the raw throughput of Layer 4 methods.
For details instructions on how to deploy each of these modes, refer to the Admin Manual below.
Example Layer 4 DR configuration
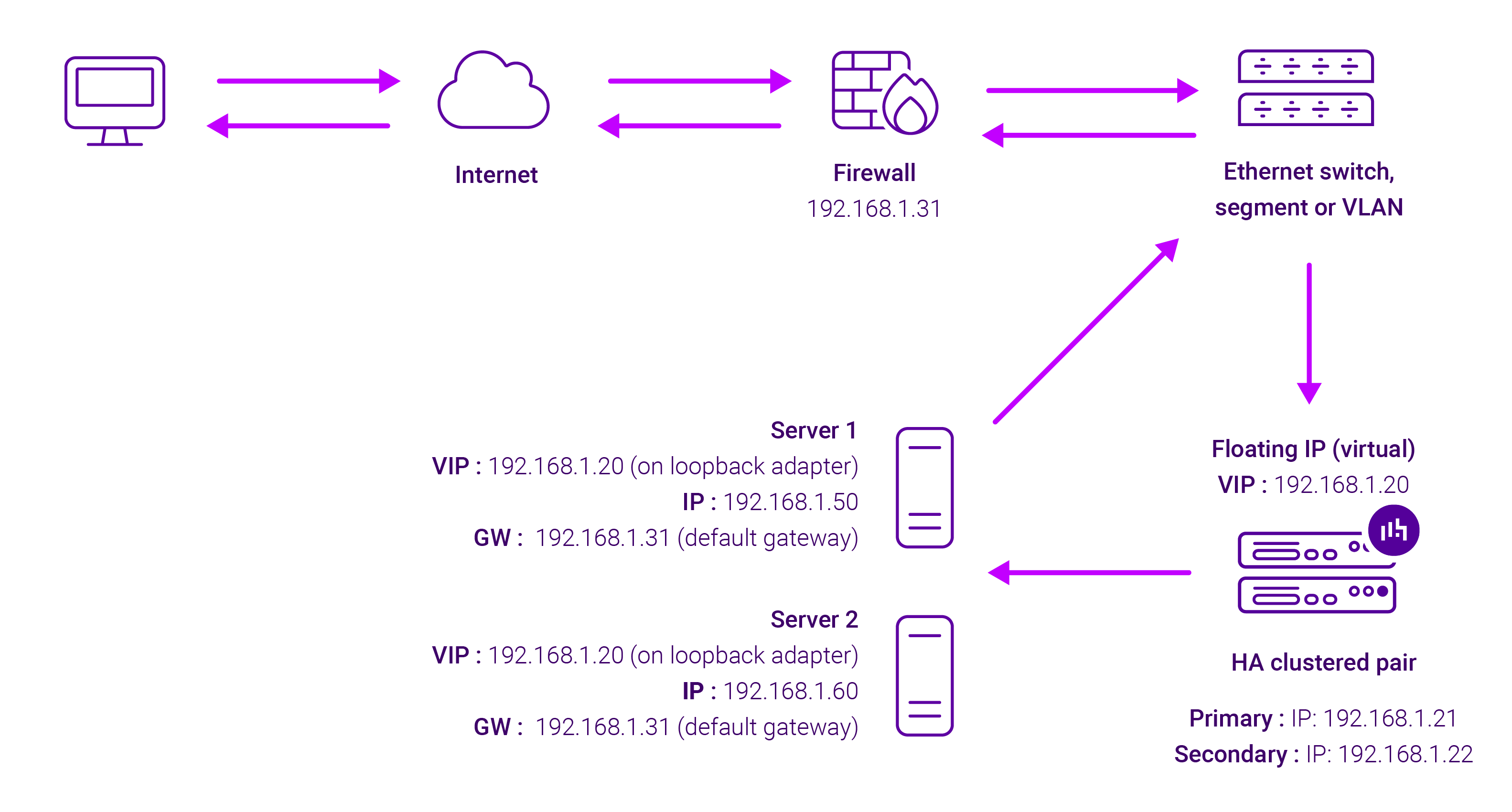
With Layer 4 Direct Routing, a node does not rely on sending its reply traffic via the load balancer. Instead, the back-end nodes have the VIP or load balancer address attached to their local interface, and so can send a TCP reply directly back to the client with the source address the client is expecting.